
North Korean developers, operating as fake freelancers, have reportedly amassed over $16.5 million this year by infiltrating crypto and traditional tech companies, according to crypto sleuth ZachXBT.
U.S. Exchanges Used to Launder Funds
According to online crypto scam investigator ZachXBT, a total of $16.58 million has been paid to North Koreans hired as developers at various projects and companies since the start of the year. ZachXBT estimates the compensation paid to these North Korean information technology workers (ITWs) to be anywhere between $3,000 and $8,000, which puts their number between 345 and 920.
In an X post sharing the probe’s findings, the investigator said, contrary to popular misconceptions, these workers are using U.S.-based crypto exchanges to launder the funds.
“A common misconception is that U.S. exchanges have more rigorous KYC/AML requirements than offshore competitors. DPRK ITWs have an increasing number of accounts tied to U.S. exchanges like Coinbase or Robinhood. MEXC remains a popular choice by ITWs for laundering funds on-chain,” the investigator stated.
ZachXBT also noted that while Binance was their go-to platform a few years ago, improvements in detection and private industry collaboration leading to seizures make the crypto exchange less appealing.
The latest findings appear to buttress earlier reports that suggested North Korean operatives posing as freelance developers looking for jobs had secured employment in crypto and Web3 firms. A report released in May by DTEX claimed that the operatives were funneling cryptocurrency back to North Korea to fund its military ambitions.
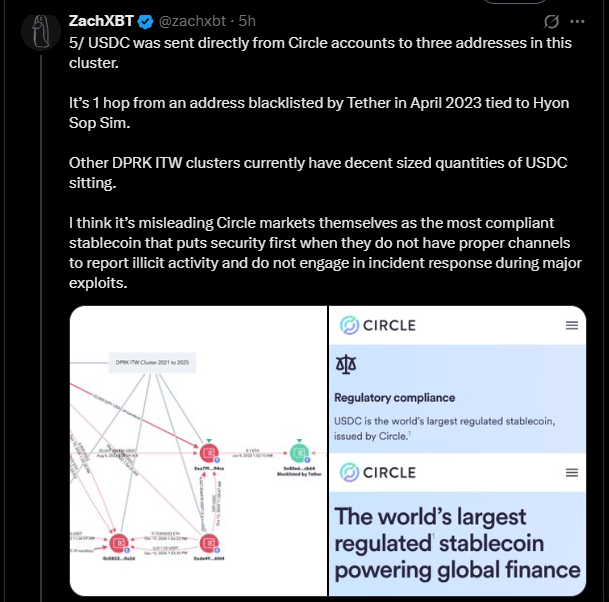
A few other reports similarly alleged that the North Korean operatives were primarily targeting crypto and Web3 companies. However, ZachXBT said his investigation, carried out for the last six months, showed traditional tech companies too had North Korean ITWs in their employ. He went on to explain why the consequences are even more dire for non-crypto companies.
“The downside of fiat is you cannot trace funds back to the company to alert them, whereas when ITWs are paid with crypto it makes all activity on-chain traceable. The rise of neobanks and fintech with stablecoin integrations has allowed DPRK ITWs to easily on-ramp fiat to crypto,” ZachXBT concluded.
The investigator, meanwhile, argued that North Korean operatives were securing employment mainly because they were “cheap.”
Source: Bitcoin



