
As sales of electric vehicles continue to surge, many new and prospective customers have questions about qualifying for federal tax credit on electric vehicles, especially now that a slew of new credits have been reinstated to US consumers (alongside their fair share of confusing and ever-evolving conditions)
Whether you qualify is not a simple yes or no question… well, actually it sort of is, but the amount you may qualify for varies by household due to a number of different factors. Furthermore, new terms implemented January 1, 2023 limit the number of EVs that currently qualify based on a number of factors pertaining to local US manufacturing.
Lastly, there are other potential savings available to you that you might not even know about yet. Luckily, we have compiled everything you need to know about tax credits for your new or current electric vehicle into one place. The goal is to help ensure you are receiving the maximum value on your carbon-conscious investment because, let’s face it, you’ve gone green and you deserve it.
Table of contents
- How does a federal tax credit work for my EV?
- A quick history lesson on the expansion of EV tax credits
- New Federal Tax Credits in the Inflation Reduction Act
- What electric vehicles could qualify for tax credit as of January 1, 2023?
- Other tax credits available for electric vehicle owners
- Tax incentives on electric vehicles are worth the research
- Electric Vehicle (EV) tax credit FAQ
How does a federal tax credit work for my EV?
The idea in theory is quite simple, per the IRS – “You may qualify for a credit up to $7,500 under Internal Revenue Code Section 30D if you buy a new, qualified plug-in EV or fuel cell electric vehicle (FCV). The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 changed the rules for this credit for vehicles purchased from 2023 to 2032.
With that said, you cannot simply go out and buy an electric vehicle and expect Uncle Sam to cut $7,500 off your taxes in April. In reality, the amount you qualify for is based on both your income tax as well as several specifications of the electric vehicle you purchase, including where it’s built. More on that below.
First, let’s take a second to truly understand how the Federal EV tax credit currently works.

How much is the federal tax credit?
First and foremost, it’s important to understand three little words the government slips in front of the $7,500 credit – “may” and “up to.” As in, you may qualify for up to $7,500 in federal tax credit for your electric vehicle. At first glance, this credit may sound like a simple flat rate, but that is unfortunately not the case.
For example, if you purchased and owed say, $3,500 in income tax this year, then that is the federal tax credit you would receive. If you owed $10,000 in federal income tax, then you would qualify for the full $7,500 credit.
It’s important to note that any unused portion of the $7,500 is not available as a refund, nor as a credit for next year’s taxes. Bummer.

A quick history lesson on the expansion of EV tax credits
Since President Joe Biden took office, the White House has introduced two bills to expand EV adoption, one of which included funding for heavily expanded EV charging infrastructure.
At the time, there were rumors that the federal tax credit would be increased to $10,000 and was quickly mentioned as a reform. The second, larger bill sat within Biden’s “Build Back Better Act” and subsequent offered increases to the federal tax credit, but it couldn’t get past the Senate in late 2021.
The revamped tax credit then sat in federal purgatory, until this past summer late July 2022 when the US Senate shared it was moving forward to vote on EV tax credit reform after Senator Joe Manchin (D-WV) finally agreed to include investments to curb climate change.
On August 7, 2022, it was approved by the Senate and a week later signed into law by President Biden. This revamped “Clean Vehicle Credit” under the Inflation Reduction Act, not only extends the length of EV tax benefits through the next decade, but also eliminates the unit threshold that some American automakers have already exhausted, thus disqualifying themselves. GM and Tesla customers rejoice! You can now join the EV tax credit party again.
Now that we are officially into 2023, the reform bill now applies to EVs purchased and delivered after December 31, 2022. Below is a breakdown of the terms of the new Clean Vehicle Credit, but be warned. Just because it’s now being implemented does not mean the US government has all of its ducks in a row yet.
These are the current qualifying terms as laid out in the IRA, however, we’ve explained how some of these requirements, in particular battery manufacturing in the US, are not currently being enforced. More on that below.
New Federal Tax Credits in the Inflation Reduction Act
- Federal tax credit for EVs will remain at $7,500
- Timeline to qualify is extended a decade from January 2023 to December 2032
- Tax credit cap for automakers after they hit 200,000 EVs sold is eliminated, making GM, Tesla, and Toyota once again eligible
- The language in the bill indicates that the tax credit could be implemented at the point of sale instead of on taxes at the end of the fiscal year
- That means you can get your credit up front at the dealer, but these terms may not kick in until 2024
- In order to get the full tax credit, the EV must be assembles in North America and…
- Two binary pieces separate the full $7,500 credit meaning the vehicle either qualifies for each piece of the credit or it doesn’t
- $3,750 of the new credit is based upon the vehicle having at least 40% of its battery critical minerals from the United States or countries with a free trade agreement with the United States. This is a list of countries with free trade agreements with the US.
- The other $3,750 of the new credit is based on at least 50% of the battery components of the vehicle coming from the United States or countries with a free trade agreement with the US
- Note – these battery requirements are now being enforced as April 18, 2023. More below.
- The 40% minerals requirement increases to 50% in 2024, 60% in 2025, 70% in 2026 and 80% in 2027
- The 50% battery components requirement increases to 60% in 2024, 70% in 2026, 80% in 2027, 90% in 2028 and 100% in 2029
- Beginning in 2025, any vehicle with battery minerals or components from a foreign entity of concern are excluded from the tax credit
- Qualifying EVs must also have a battery size of at least 7 kWh and a gross vehicle weight rating less than 14,000 pounds
- New federal tax credit of $4,000 for used EVs priced below $25k
- Subject to other requirements like lower annual income (see below)
- Revised credit applies to battery electric vehicles with an MSRP below $55,000
- Also includes zero-emission vans, SUVs, and trucks with MSRPs up to $80,000
- New credit also expands to commercial fleet customers
- Includes separate qualifications and limits
- The federal EV tax credit will be available to individuals reporting adjusted gross incomes of $150,000 or less, $225,000 for heads of households, or $300,000 for joint filers
- The new credit will also continue to apply to Plug-in Hybrid EVs (PHEVs) as long as they meet the same requirements outlined above
Revamped used vehicle credit
Used EVs also got revised terms that now offers a credit equal to 30% percent of the sale price (up to $4,000). That should help consumers like yourselves get some change back in your pocket at the end of the fiscal year. As long as you stick to these terms as outlined by the IRS.
To qualify as a customer, you must:
- Be an individual who bought the vehicle for use and not for resale
- Not be the original owner
- Not be claimed as a dependent on another person’s tax return
- Not have claimed another used clean vehicle credit in the three years before the EV purchase date
- Modified adjusted gross income must not exceed $75k for individuals, $112,500 for heads of households, and $150k for joint returns
For the used EV to qualify for federal tax credits, it must:
- Have a sale price of $25,000 or less
- Have a model year at least two years earlier than the calendar year when you buy it
- For example, a vehicle purchased in 2023 would need a model year of 2021 or older
- Not have already been transferred after August 16, 2022, to a qualified buyer
- Have a gross vehicle weight rating of less than 14,000 pounds
- Be an eligible FCV or plug-in EV with a battery capacity of least 7 kilowatt hours (kWh)
- Be for use primarily in the United States
- You buy the vehicle from a dealer
- For qualified used EVs, the dealer reports required information to you at the time of sale and to the IRS
- Purchaser must be an individual (no businesses) to qualify for used credit
- A used vehicle qualifies for tax credit only once in its lifetime

What electric vehicles could qualify for tax credit as of January 1, 2023?
Alright, this is probably the main reason why you’re here. If you scrolled through the details above, you may want to consider going back and at least skimming, because there are some major changes to federal tax credits to electric vehicles under the Inflation Reduction Act.
Following a revision by the IRS, the US department of Treasury delayed its battery guidance pertaining to what EV manufactures need to build in the US for their vehicles to qualify. Although the department was given a deadline of December 2022 to deliver this guidance, it relayed that it neededd more time, at least until March of 2023.
As a result, the qualifying factors mentioned above that pertain to battery component assembly and materials being sourced and built in North America are not being enforced… at least not until April 18, 2023. Just recently, the US Department of Treasury has finally shared its battery guidance for qualifying EVs, here’s the latest
Battery guidance update as of April 2023
Following a near four month delay, the US government has shared its guidance as to what parameters surrounding battery component assembly and their respective materials will be required for a given EV to still qualify for federal tax credits.
Now, EV manufacturers must ensure that battery critical minerals used in vehicles assembled in America are also “extracted or processed in the US or any country with which the US has a free trade agreement,” or recycled in North America. Like the EV themselves, battery components must also be “manufactured or assembled in North America.”
To date, the following countries are recognized by local government as US free trade partners: Australia, Bahrain, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Dominican Republic, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Israel, Jordan, Korea, Mexico, Morocco, Nicaragua, Oman, Panama, Peru, Singapore, and Japan.
In addition to the new trade agreement with Japan, the US is in talks with the EU to enact a similar agreement so more EVs from from automakers across the pond eventually qualify… even if they are simultaneously investing time and money into arguably obsolete technology like carbon-neutral combustion cars.
Each of the two newly enforced qualifying factors account for $3,750 in tax credits, combining for the total $7,500. Additionally, each of the battery factors contain an “applicable percentage” based on the year the vehicle is placed into service. Rather than basing an EV’s qualifications on factors like battery weight or capacity like in years past, the new process measures the overall value of each component or mineral used in the battery supply chain.
Not sure if your prospective EV purchase qualifies? We can’t blame you. Here’s a handy flowchart we made to help (hopefully) simplify the details for you.
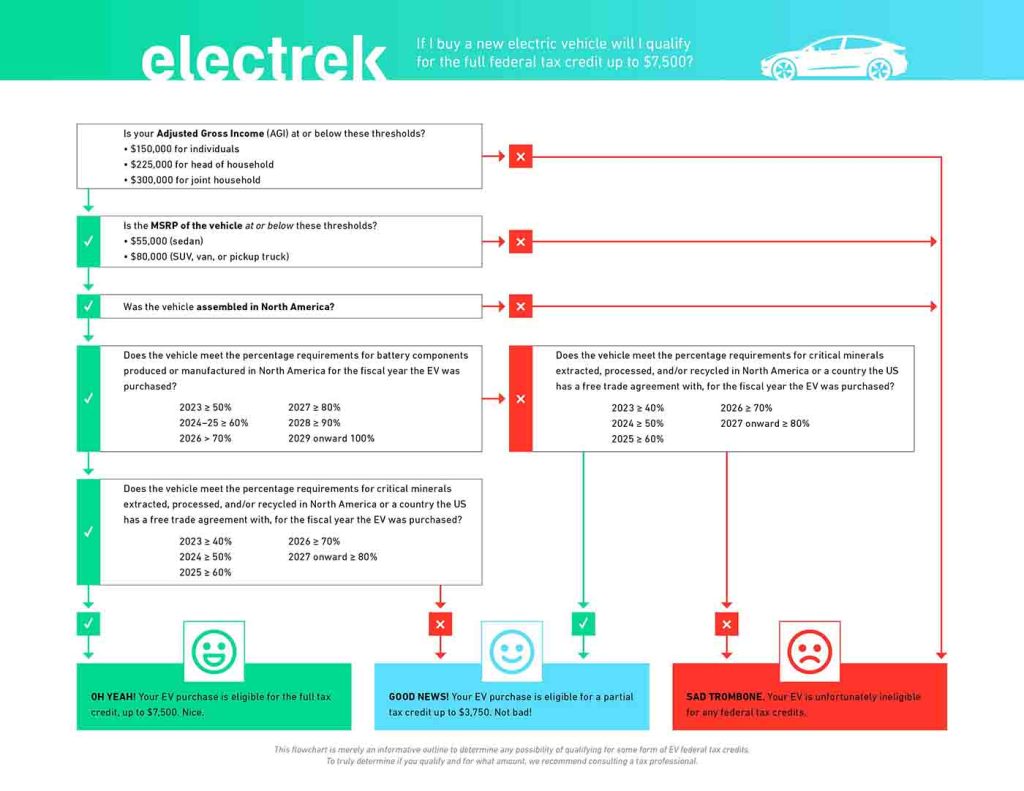
Another important factor to take note of in the Treasury’s battery guidance is that after 2024, batteries must contain zero components manufactured or assembled by a foreign entity of concern (FEOC). After, no critical minerals can be extracted, processed, or recycled by an FEOC. The Us government has yet to share a specific list of FEOCs, but the Dept. of Treasury has once again vowed to deliver those details before year’s end.
The battery guidance currently sits as a proposed rule that has been published in the federal register, leaving the door open for public feedback until June 16, 2023 before taking its final form. Still, the proposed qualifying factors are in effect as of April 18, 2023 while the finalized iteration is solidified. Any future changes are expected to be minor, but we will be sure to keep you in the know,
Under the terms mentioned above, these are the EVs that could qualify for the some for of the federal EV tax credit. Notice several previously qualifying models have been struck through per the guidance of the US Treasury as of April 18, 2023.
All-electric vehicles
| Make and Model | MSRP Limit | Tax Credit Amount |
| CADILLAC (GM) | ||
| Lyriq (2023-2024) | $80,000 | Up to $7,500 |
| CHEVROLET (GM) | ||
| Blazer EV (2024) | $55,000 | Up to $7,500 |
| Bolt EUV (2022-2023) | $55,000 | Up to $7,500 |
| Bolt EV (2022-2023) | $55,000 | Up to $7,500 |
| Equinox EV (2024) | $55,000 | Up to $7,500 |
| Silverado EV (2024) | $80,000 | Up to $7,500 |
| FORD | ||
| F-150 Lightning (2022-2023) | $80,000 | Up to $7,500 |
| Mustang Mach-E (2022-2023) | $80,000 | Up to $3,750 |
| E-Transit (2022-2023) | $80,000 | Up to $3,750 |
| RIVIAN | ||
| R1T (2023) | $80,000 | Up to $3,750 |
| R1S (2023) | $80,000 | Up to $3,750 |
| TESLA | ||
| Model 3 Standard Range RWD/Long Range (2022-2023) | $55,000 | Up to $3,750 |
| Model 3 Performance (2022-2023) | $55,000 | Up to $7,500 |
| Model Y AWD/Long Range/Performance (2022- 2023) | $80,000 | Up to $7,500 |
| VOLKSWAGEN | ||
| ID.4 / ID.4 S (2023) | $80,000 | $7,500 |
| ID.4 Pro/Pro S/Pro S Plus (2023) | $80,000 | $7,500 |
| ID.4 AWD Pro/AWD Pro S/AWD Pro S Plus (2023) | $80,000 | $7,500 |

Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles
| Make and Model | MSRP Limit | Full Tax Credit |
| CHRYSLER | ||
| Pacifica Plug-in Hybrid (2022-2023) | $80,000 | Up to $7,500 |
| FORD | ||
| Escape Plug-in Hybrid (2022-2023) | $80,000 | Up to $3,750 |
| JEEP | ||
| Grand Cherokee 4xe (2022-2023) | $80,000 | Up to $3,750 |
| Wrangler 4xe (2022-2023) | $80,000 | Up to $3,750 |
| LINCOLN | ||
| Aviator Grand Touring (2022-2023) | $80,000 | Up to $7,500 |
| Corsair Grand Touring (2022-2023) | $80,000 | Up to $3,750 |
Other tax credits available for electric vehicle owners
So now you should know if your vehicle does in fact qualify for a federal tax credit, and how much you might be able to save.
Find out where an EV is assembled using its VIN
The US Department of Energy offers a VIN decoder tool to confirm where a given EV is assembled. Check it out here.
Check out our complete breakdown of state tax incentives, sorted by state
In additional to any federal credit you may or may not qualify for, there are a number of clean transportation laws, regulations, and funding opportunities available at the state level.
For example, in the state of California, drivers can qualify for a $2,000-$4,500 rebate or a grant up to $5,000 under the Clean Vehicle Assistance Program on top of any federal credit received (all rebate and grant amounts are based on income). These incentives vary by state, and much like the federal tax credit, are contingent on multiple factors.
Want to learn more? Of course you do! Luckily, we’ve compiled each and every state rebate, tax credit, and exemption for you and sorted it by state. Whether its a purchase or lease of a new or used
EV, or the purchase and/or installation of an EV charger, you could get money back, depending where you live.
Here are all those tax credits, rebates, and exemptions, sorted by state.
Tax incentives on electric vehicles are worth the research
Hopefully this post has helped to incentivize you to use the resources above to your advantage.
Whether it’s calculating potential savings or rebates before making a new EV purchase or determining what tax credits might already be available to you for your current electric vehicle, there is much to discover.
Ditching fossil fuels for greener roadways should already feel rewarding, but right now the government is willing to reward you further for your environmental efforts.
Use it to your full capability while you can, because as more and more people start going electric, the less the government will need to reward drivers.
Electric Vehicle (EV) tax credit FAQ
At the federal level, the tax credits for EVs (electric cars, vans, trucks, etc) operates as money back at the end of the fiscal year you purchased or leased your vehicles based on a number of factors.
The awarded credit is up to $7,500 per vehicle, but how much you may get back will depend on the your annual income, whether you are filing with someone else like a spouse, and what electric vehicle you purchased.
For example, if you purchased a Ford Mustang Mach-E and owed $3,500 in income tax this year, then that is the federal tax credit you would receive. If you owed $10,000 in federal income tax, then you could qualify for the full $7,500 credit.
It’s important to note that any unused portion of the $7,500 is not available as a refund, nor as a credit for next year’s taxes.
You may also be able to receive money back right away as a point of sale credit, but those terms probably won’t kick in until 2024 at the earliest.
As things currently stand, there is a lot up in the air right now. The first table above details all of the electric vehicles that qualify under terms of the Inflation Reduction Act. However, battery guidance has now been updated has kicked in So this ever-evolving list will continue to change. Be sure to check the date at the bottom of each table above to see when it was most recently updated.
As previously mentioned, qualifying terms for electric vehicle became more strict with the start of 2023, and EVs and their battery components must be assembled in North America to qualify.
As you can see above, significantly fewer electric vehicles qualify under the new terms, but as time goes on, more and more automakers will adapt their production strategies to operate within North America and start selling vehicles that qualify.
American companies like Ford, GM, and Tesla already have EVs that qualify to some extent, but others are sure to follow. We will continually update the list above as we learn more.
Excellent question. Since traditional hybrid vehicles rely primarily on combustion and do not use a plug to charge, they do not qualify for tax credits at the federal level. Credits apply to plug-in electric vehicles which includes plug-in hybrid EVs and battery electric vehicles (BEVs).
Yes! Under revised terms in the inflation reduction act. Used EVs will now qualify in addition to new vehicles as previously stated.
Starting January 1, 2023 qualifying used EVs priced below $25,000 can qualify for up to $4,000 in federal tax credits. There are some terms to note however:
– Used vehicle qualifies for tax credit only once in its lifetime.
– Purchaser must be an individual (no businesses) to qualify for the used vehicle credit.
– Purchaser may only claim one used vehicle credit per three years.
– Used vehicle must be at least two model years old at time of sale.
– The original use of the vehicle must have occurred with an individual other than the one claiming the used tax credit.
– Used vehicle must be purchased from a dealer.
– Gross income cap of $75k for individuals, $112,500 for heads of households, and $150k for joint returns.
– Credit may be applied at time of sale by dealer
Yes.
Under the new terms in the Inflation reduction act, the MSRP of electric vehicle must be $80,000 or less for SUVs, vans, and trucks. MSRPs for all other electric vehicles must be $55,000 or less.
Modified adjusted gross income limits are $150,000 for individuals, $225,000 for heads of households, and $300,000 for joint returns. Any reported annual income below these thresholds should qualify you for some level of tax credit, as long as your new purchase is a qualifying electric vehicle.
Author: Scooter Doll
Source: Electrek




Top comment by betterbruce
Liked by 51 people
Y’all keep reposting this article trying to keep up with the updates to the tax code and I appreciate the desire to be thorough and update old information but I find this format too cumbersome to be helpful. I think it would make more sense to post new articles each time such as “here are the BEVs that qualify AS OF <>”.
1) It removes the need to have a section in current article about the old rules that have expired. People can refer to an old article if needed.
2) Because I know the article has been updated many times, I don’t feel like I can trust any use of the word “current” in it. I see sentences that say “current” and I have to wonder if that is truly current or if it’s an accidental leftover word from when the article was published months ago.
Even ignoring historical guidance, there’s too much here. Fuel cell vehicles? BEVs under 7kWh or over 14k lbs? How many people are looking for those/ how useful is it to include this, particularly all lumped into a single article? Maybe that’s useful detail but doesn’t seem necessary for most consumers.
While I’m on that topic, you can probably split out BEV/ PHEV as separate articles too, because most people aren’t cross-shopping them.
Last thought: if it is possible to make a flowchart or an “internet quiz” on whether a car qualifies, that could be very useful. “is it a BEV, PHEV, or fuel cell vehicle…” > “Does it have more than 7kWh battery?”… etc.
View all comments